List your products on these platforms for enhanced global reach
Create your B2B product catalogue on GlobalLinker Marketplace
An initiative of the Government of India to compete with large market players

An intiative by IDMA & MAS, Singapore, to enable cross-border B2B trade for MSMEs
An intiative of FIEO for Indian exporters and foreign buyers
Popular Categories
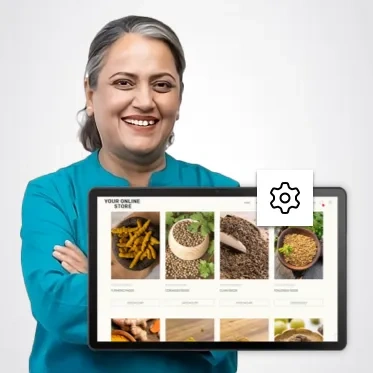
Start selling online with a comprehensive ecommerce solution.

List your products on multiple marketplaces and grow your global visibility and reach.
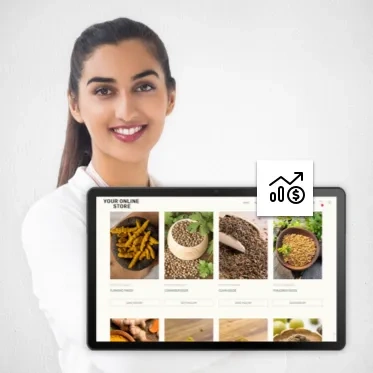
Analyse and optimise your store performance to grow your business.
One Listing, Many Marketplaces
Create your catalogue on GlobalLinker and list your products on multiple marketplaces

B2B Feature Catalogue
Extend, manage & track credit cycle and discounts with exclusive B2B access for your trusted buyers, agents, and dealers

Secure B2B Payments
Accept multi currency payments from different payment methods or with a digital escrow account (Coming Soon)
Give your SME clients a B2B marketplace with powerful tools and resources on our global networking platform while offering your products or services to them
Partner With UsOffer your products or services, on preferred terms, to our SME Members in a specific country or around the world.
Partner With UsGlobalLinker Seller Platform is a comprehensive digital platform that empowers businesses to create, manage, and scale their online catalogues. By digitising your product listings, you can enhance your online presence and reach a global audience through seamless integration with multiple sales channels.
Signing up on GlobalLinker Seller Platform allows you to:
The platform provides essential tools for efficient business management, networking with potential buyers and suppliers, and expanding your reach through various sales channels.
On GlobalLinker Seller Platform, you can connect with potential buyers by optimising your digital catalogue, joining relevant sales channels, and participating in the community. The platform enables you to respond quickly to inquiries and orders and network with other business owners to grow your business.
GlobalLinker Seller Platform integrates with multiple marketplaces:
This gives you access to a wider market and allows you to convert your catalogue into an eCommerce store.
GlobalLinker Seller Platform offers real-time notifications for inquiries and orders, ensuring you can respond promptly and maintain high customer satisfaction.
GlobalLinker Seller Platform offers community features that enable you to network with other business owners, participate in discussions, share insights, and collaborate on business opportunities.